In this post, we will see How to write custom method in the repository in Spring Data JPA. We will cover the below points in this post. Also, we will see some basic rules to define query/repository method using different keywords.
- Write query/repository method using different keywords(And, Or, Between etc.).
- Write query method using @Query annotation.
- Write query method using Named Parameters.
- Write query method using JPA @NamedQuery and @NamedNativeQuery.
Write query/repository method using different keywords(And, Or, Between etc.).
Rules to define query/repository method using different keywords.
Consider we have an entity called Student.java and we have some records in the database as below.
Student.java
package com.javatute.entity;
@Entity
public class Student {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private int id;
@Column(name = "name")
private String name;
@Column(name = "roll_number")
private String rollNumber;
@Column(name = "university")
String university;
}
Record in the database as below.

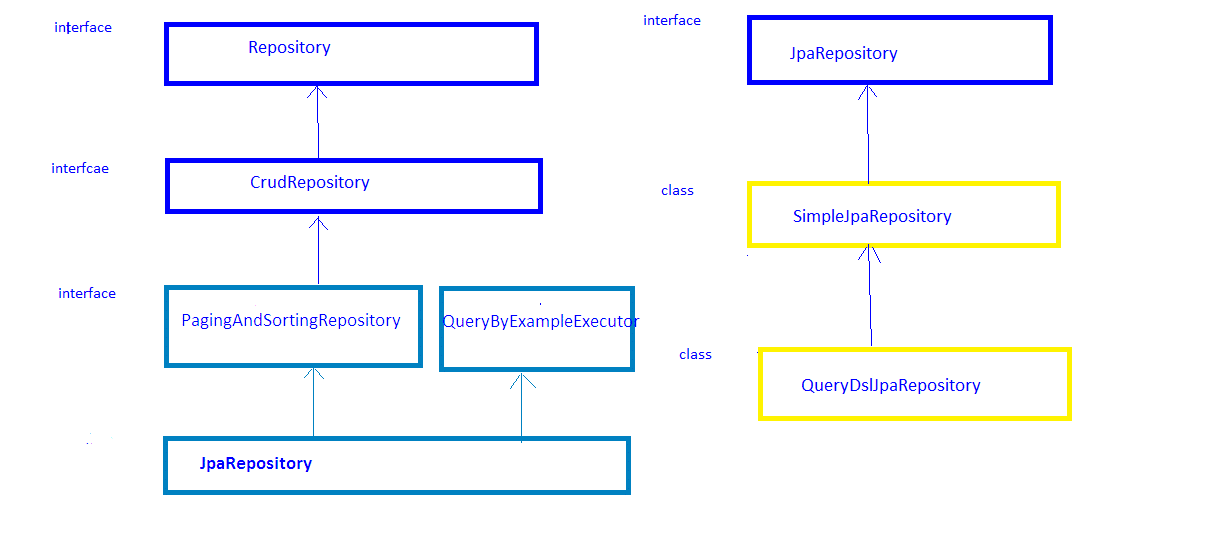
To write query methods first we need to define custom repository interface extending CrudRepository or JpaRepository interface.
@Repository
public interface StudentRepository extends JpaRepository<Student, Serializable> {
}
Rules to define Query methods.
Rule 1 – The name of the query method must start with findBy or getBy or queryBy or countBy or readBy prefix. The findBy is mostly used by the developer.
for example.
Below query methods are valid.
public List<Student> findByName(String name);
public List<Student> getByName(String name);
public List<Student> queryByName(String name);
public List<Student> countByName(String name);
public List<Student> readByName(String name);
Note – All the above query methods will return all students whose name is “what ever name we provide as parameter”.
Rule 2 – The first character of field name should capital letter. Although if we write the first character of the field in small then it will work but we should use camelcase for the method name.
Both are valid query method defined below but we should follow the first way.
public List<Student> findByName(String name);
public List<Student> findByname(String name);
Rule 3 – While using findBy or getBy or queryBy or countBy or readBy the character B must be in capital letter, else we will get an exception while deployment.
Caused by: org.springframework.data.mapping.PropertyReferenceException: No property querybyName found for type Student!
Invalid query method.
public List<Student> findbyName(String name);
Rules 4 – We can write the query method using multiple fields using predefined keywords(eg. And, Or etc) but these keywords are case sensitive. We must use “And” instead of “and”.
For example, we want to fetch all students on the basis of the name and rollNumber.
Valid query method.
public List<Student> findByNameAndRollNumber(String name, String rollNumber);
Invalid query method.
public List<Student> findByNameandRollNumber(String name, String rollNumber);
if you use public List<Student> findByNameandRollNumber(String name, String rollNumber); will get below exception.
Caused by: org.springframework.data.mapping.PropertyReferenceException: No property nameandRollNumber found for type Student
Rule 5 – We can write the query method if we want to restrict the number of records by directly providing the number as the digit in method name. We need to add the First or the Top keyword before the by and after find.
public List<Student> findFirst3ByName(String name);
public List<Student> findTop3ByName(String name);
Both query methods will return only first 3 records.
List of keywords used to write custom repository methods.
And, Or, Is, Equals, Between, LessThan, LessThanEqual, GreaterThan, GreaterThanEqual, After, Before, IsNull, IsNotNull, NotNull, Like, NotLike, StartingWith, EndingWith, Containing, OrderBy, Not, In, NotIn, True, False, IgnoreCase.
Let’s see some example of the custom query/repository methods.
package com.javatute.repository;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.javatute.entity.Student;
@Repository
public interface StudentRepository extends JpaRepository<Student, Serializable> {
public List<Student> findFirst3ByName(String name);
public List<Student> findByNameIs(String name);
public List<Student> findByNameEquals(String name);
public List<Student> findByRollNumber(String rollNumber);
public List<Student> findByUniversity(String university);
public List<Student> findByNameAndRollNumber(String name, String rollNumber);
public List<Student> findByRollNumberIn(List<String> rollNumbers);
public List<Student> findByRollNumberNotIn(List<String> rollNumbers);
public List<Student> findByRollNumberBetween(String start, String end);
public List<Student> findByNameNot(String name);
public List<Student> findByNameContainingIgnoreCase(String name);
public List<Student> findByNameLike(String name);
public List<Student> findByRollNumberGreaterThan(String rollnumber);
public List<Student> findByRollNumberLessThan(String rollnumber);
}
Let’s see other ways to write custom method in repository.
Write query method using @Query.
Writing JPQL using Spring Data Jpa @Query.
@Query("select s from Student s where s.name = ?1")
List<Student> getStudents(String name);
See a complete example of the JPQL using Spring Boot and Oracle here.
Writing the Named Parameter @Query.
@Query("select s from Student s where s.name = :name")
List<Student> findByName(@Param("name") String name);
See a complete example of the Named Parameter using Spring Boot and Oracle here.
Write query method using JPA @NamedQuery and @NamedNativeQuery.
- Spring Data JPA greater than Example
- Spring Data JPA less than Example
- Spring Data JPA IsNull Example Using Spring Boot
- Spring Data findById() Vs getOne()
- Spring Data JPA CrudRepository findById()
- Spring Data JPA JpaRepository getOne()
- Spring Data CrudRepository saveAll() and findAll().
- Spring Data CrudRepository existsById()
- Spring Data JPA delete() vs deleteInBatch()
- Spring Data JPA deleteAll() Vs deleteAllInBatch()
- Spring Data JPA JpaRepository deleteAllInBatch()
- Spring Data JPA deleteInBatch() Example
- Spring Data JPA JpaRepository saveAndFlush() Example
- Spring Data JPA CrudRepository count() Example
- Spring Data JPA CrudRepository delete() and deleteAll()
- Spring Data JPA CrudRepository deleteById() Example
- CrudRepository findAllById() Example Using Spring Boot
- Spring Data CrudRepository save() Method.
- Sorting in Spring Data JPA using Spring Boot.
- Spring Data JPA example using spring boot.
- Spring Data JPA and its benefit.
Other Spring Data JPA and Hibernate tutorials.
- @Version Annotation Example In Hibernate.
- Hibernate Validator Constraints Example Using Spring Boot.
- @Temporal Annotation Example In Hibernate/Jpa Using Spring Boot.
- Hibernate Table Per Concrete Class Spring Boot.
- Hibernate Table Per Subclass Inheritance Spring Boot.
- Hibernate Single Table Inheritance using Spring Boot.
- One To One Mapping Annotation Example in Hibernate/JPA using Spring Boot and Oracle.
- One To One Bidirectional Mapping Example In Hibernate/JPA Using Spring Boot and Oracle.
- One To Many Mapping Annotation Example In Hibernate/JPA Using Spring Boot And Oracle.
- Many To One Unidirectional Mapping In Hibernate/JPA Annotation Example Using Spring Boot and Oracle.
- One To Many Bidirectional Mapping In Hibernate/JPA Annotation Example Using Spring Boot and Oracle.
- Many To Many Mapping Annotation Example In Hibernate/JPA Using Spring Boot And Oracle.
Spring Data JPA Docs.
Summary – We have seen how to write custom method in repository in Spring Data JPA



