Here we will see @RequestMapping annotation example In Spring Boot.
- This annotation introduced in Spring 2.5, available in org.springframework.web.bind.annotation package.
- It has optional elements consumes, headers, method, name, params, path, produces and value.
- We use this annotation with the class as well as method.
Let’s see an example of @RequestMapping.
prerequisites –
- JDK 1.8
- Eclipse
- maven
- postman
Create maven project, Don’t forget to check ‘Create a simple project (skip)’click on next. Fill all details(GroupId – requestmappigexamle, ArtifactId – requestmappigexamle and name – requestmappigexamle) and click on finish. Keep packaging as the jar.
pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>requestmappigexamle</groupId>
<artifactId>requestmappigexamle</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>requestmappigexamle</name>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.2.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
Define Contoller(Book.java), SpringBootMain(BookMain.java), and Entity class(BookController.java).
Book.java
package requestmappigexamle;
public class Book {
int bookId;
String bookName;
String bookPrice;
public int getBookId() {
return bookId;
}
public void setBookId(int bookId) {
this.bookId = bookId;
}
public String getBookName() {
return bookName;
}
public void setBookName(String bookName) {
this.bookName = bookName;
}
public String getBookPrice() {
return bookPrice;
}
public void setBookPrice(String bookPrice) {
this.bookPrice = bookPrice;
}
}
The controller class for @RequestMapping annotation example In Spring Boot.
BookController.java
package requestmappigexamle;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/test")
public class BookController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/simpleuri",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public Book getBook() {
Book book = new Book();
book.setBookId(109);
book.setBookName("book1");
book.setBookPrice("100");
return book;
}
}
BookMain.java
package requestmappigexamle;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.domain.EntityScan;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class BookMain {
public static void main(final String[] args) {
final ConfigurableApplicationContext configurableApplicationContext = SpringApplication
.run(BookMain.class, args);
}
}
If you encounter any port related issue, define application.properties and change the port.
application.properties
server.port = 9093
Let’s run the BookMain.java and deploy the application.
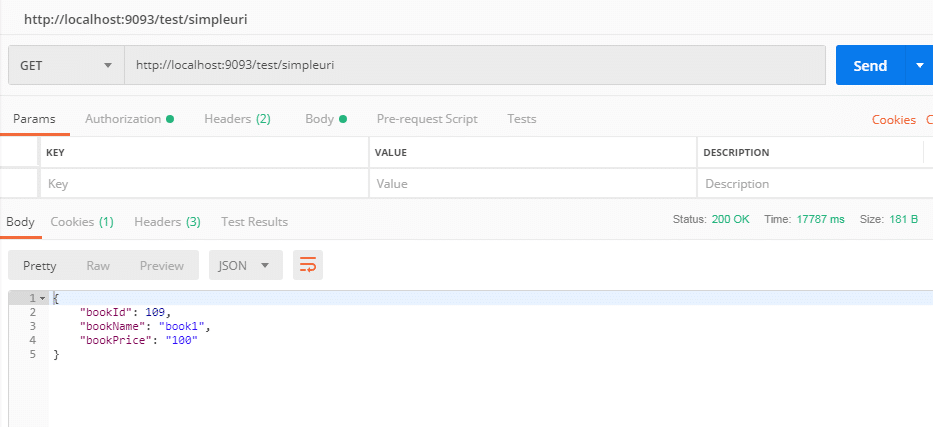
Let’s test the URI –
In the above example, we can see @RequestMapping annotation we are with the class as well as method. Also, we have seen two elements value and method.
Now suppose we want to produce XML instead of JSON, let’s modify the controller class.
package requestmappigexamle;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/test")
public class BookController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/simpleuri",method = RequestMethod.GET,produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_XML_VALUE)
public String getBookAsXml() {
return "<Book>bookname1</Book>";
}
}
Although this is not a proper way to produce XML (See here how to produce XML response in real time development), here mainly we are discussing @RequestMapping and its elements. The same way we can reproduce JSON data.
That’s all about @RequestMapping annotation example In Spring Boot.
You may like.
- @RestController and @Controller annotation example in Spring Boot.
- @RequestBody and @ResponseBody annotation example in Spring Boot.
- @PathVariable and @RequestParam annotations in Spring Boot.
- @RequestHeader annotation example by using Spring Boot.
- @SpringBootApplication annotation example in Spring Boot.
- @Component, @Controller, @Service and @Repository annotations example using Spring Boot.
- @Configuration annotation example using spring boot.
- @ComponentScan example in spring boot.
- Spring Boot interceptor example.
- Filter example in Spring Boot.
- Deploy Spring boot war in JBoss EAP server.
- Jboss 7 EPA datasource configuration using oracle and spring boot.
- Deploy Spring Boot application on external Tomcat.
Spring @RequestMapping docs.