In this article, we will see about Spring Data JPA CrudRepository delete() and deleteAll() methods example using Spring Boot and oracle.
The delete() method is used to delete a single entity which we pass as request data and it is available in CrudRepository interface. The CrudRepository extends Repository interface. In Spring Data JPA Repository is top-level interface in hierarchy. Here we are going to see delete() and deleteAll() method of CrudRepository. Let’s see about delete() method. The delete() method has been defined as below.
void delete(T entity);
Using delete() method we can delete a single record(entity). If we don’t provide any entity it will throw IllegalArgumentException.
Internally delete() method use EntityManger’s remove() method.
public void delete(T entity) {
em.remove(entity);
}
we wil
The deleteAll() method has two overloaded versions.
First one – void deleteAll(Iterable<? extends T> entities)
Using the above method we can delete all entities which we pass as request data. The deleteAll() internally use delete() method only.
public void deleteAll(Iterable<? extends T> entities) {
for (T entity : entities) {
delete(entity);
}
}
Second one – void deleteAll()
The above one will delete all records that belong to that repository. The deleteAll() internally uses findAll() and delete() method as below.
public void deleteAll() {
for (T element : findAll()) {
delete(element);
}
}
Let’s see in below code how to use the Spring Data JPA CrudRepository delete() and deleteAll() method for delete operation.
package com.javatute.impl;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import com.javatute.entity.Student;
import com.javatute.repository.StudentRepository;
import com.javatute.service.StudentService;
@Service("studentServiceImpl")
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService {
@Autowired
private StudentRepository studentRepository;
@Transactional
public List<Student> saveAllStudent(List<Student> studentList) {
List<Student> response = (List<Student>) studentRepository.saveAll(studentList);
return response;
}
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public List<Student> getAllStudents() {
List<Student> studentResponse = (List<Student>) studentRepository.findAll();
return studentResponse;
}
@Transactional
public void delete(Student student) {
studentRepository.delete(student);
}
@Transactional
public void deleteAllPassingEntities(List<Student> students) {
studentRepository.deleteAll(students);
}
@Transactional
public void deleteAll() {
studentRepository.deleteAll();
}
}
Before go ahead see brief about Spring Data JPA Repository hierarchy as below.

Let’s see an example of Spring Data JPA CrudRepository delete() and deleteAll() Example where we will use saveAll() method for creating the entities, findAll() to get all record, delete() to delete a single record and deleteAll() to delete all records.
Open eclipse and create maven project, Don’t forget to check ‘Create a simple project (skip)’ click on next. Fill all details(GroupId – springdatadeleteanddeleteall, ArtifactId – springdatadeleteanddeleteall and name – springdatadeleteanddeleteall) and click on finish. Keep packaging as the jar.
Modify pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>springdatadeleteanddeleteall</groupId>
<artifactId>springdatadeleteanddeleteall</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>springdatadeleteanddeleteall</name>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.2.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.oracle</groupId>
<artifactId>ojdbc6</artifactId>
<version>11.2.0.3</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>${project.artifactId}</finalName>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.1</version>
<configuration>
<fork>true</fork>
<executable>C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_131\bin\javac.exe</executable>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Note – In pom.xml we have defined javac.exe path in configuration tag. You need to change accordingly i.e where you have installed JDK.
If you see any error for oracle dependency then follow these steps.
Directory structure –

Student.java
package com.javatute.entity;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
@Entity
public class Student {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private int id;
@Column(name = "name")
private String name;
@Column(name = "roll_number")
private String rollNumber;
@Column(name = "university")
String university;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getRollNumber() {
return rollNumber;
}
public void setRollNumber(String rollNumber) {
this.rollNumber = rollNumber;
}
public String getUniversity() {
return university;
}
public void setUniversity(String university) {
this.university = university;
}
}
StudentController.java
package com.javatute.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.javatute.entity.Student;
import com.javatute.service.StudentService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/student")
public class StudentController {
@Autowired
private StudentService studentService;
@RequestMapping(value = "/saveall", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public List<Student> saveAllStudents(@RequestBody List<Student> studentList) {
List<Student> studentResponse = (List<Student>) studentService.saveAllStudent(studentList);
return studentResponse;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/getall", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public List<Student> getAllStudents() {
List<Student> studentResponse = (List<Student>) studentService.getAllStudents();
return studentResponse;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/delete", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@ResponseBody
public String delete(@RequestBody Student student) {
studentService.delete(student);
return "Successfully deleted single record";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/deleteallpassingentitiesasrequest", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@ResponseBody
public String deleteAllPassingEntities(@RequestBody List<Student> students) {
studentService.deleteAllPassingEntities(students);
return "Successfully deleted all enitities which has been passed as request data";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/deleteall", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@ResponseBody
public String deleteAll() {
studentService.deleteAll();
return "Successfully deleted all enitities";
}
}
StudentRepository.java – interface
Let’s see about Spring Data JPA CrudRepository deleteById().
package com.javatute.repository;
import java.io.Serializable;
import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.javatute.entity.Student;
@Repository
public interface StudentRepository extends CrudRepository<Student, Serializable> {
}
StudentService.java – interface
package com.javatute.service;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import com.javatute.entity.Student;
@Component
public interface StudentService {
public List<Student> saveAllStudent(List<Student> studentList);
public List<Student> getAllStudents();
public void delete(Student student);
public void deleteAllPassingEntities(List<Student> student);
public void deleteAll();
}
StudentServiceImpl.java
package com.javatute.impl;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import com.javatute.entity.Student;
import com.javatute.repository.StudentRepository;
import com.javatute.service.StudentService;
@Service("studentServiceImpl")
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService {
@Autowired
private StudentRepository studentRepository;
@Transactional
public List<Student> saveAllStudent(List<Student> studentList) {
List<Student> response = (List<Student>) studentRepository.saveAll(studentList);
return response;
}
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public List<Student> getAllStudents() {
List<Student> studentResponse = (List<Student>) studentRepository.findAll();
return studentResponse;
}
@Transactional
public void delete(Student student) {
studentRepository.delete(student);
}
@Transactional
public void deleteAllPassingEntities(List<Student> students) {
studentRepository.deleteAll(students);
}
@Transactional
public void deleteAll() {
studentRepository.deleteAll();
}
}
SpringMain.java
package com.javatute.main;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.domain.EntityScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
@SpringBootApplication
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.*")
@EntityScan("com.javatute.entity")
public class SpringMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringMain.class, args);
}
}
N
JpaConfig.java
package com.javatute.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.config.EnableJpaRepositories;
@Configuration
@EnableJpaRepositories(basePackages = "com.javatute.repository")
public class JpaConfig {
}
application.properties
# Connection url for the database spring.datasource.url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:XE spring.datasource.username=SYSTEM spring.datasource.password=oracle2 spring.datasource.driver-class-name=oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver # Show or not log for each sql query spring.jpa.show-sql = true spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto =create spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.Oracle10gDialect server.port = 9091
Let’s run the SpringMain class(run as java application).
Perform save operation first using below REST API.
Request Data –
[
{
"name": "Hiteshdo",
"rollNumber": "0126CS01",
"university":"rgtu"
},
{
"name": "Johnhjhjhjhj",
"rollNumber": "0126CS02",
"university":"rgtu"
},
{
"name": "Mohankkkkkkkkkkkkkk",
"rollNumber": "0126CS03",
"university":"rgtu"
},
{
"name": "Nagesh",
"rollNumber": "0126CS04",
"university":"rgtu"
},
{
"name": "s",
"rollNumber": "0126CS05",
"university":"rgtu"
},
{
"name": "Ranakum",
"rollNumber": "0126CS06",
"university":"rgtu"
},
{
"name": "Roc",
"rollNumber": "0126CS07",
"university":"rgtu"
},
{
"name": "Simpy",
"rollNumber": "0126CS08",
"university":"rgtu"
},
{
"name": "Tiwari",
"rollNumber": "0126CS09",
"university":"rgtu"
}, {
"name": "Appu",
"rollNumber": "0126CS10",
"university":"rgtu"
},
{
"name": "Babloo",
"rollNumber": "0126CS11",
"university":"rgtu"
},
{
"name": "Ga",
"rollNumber": "0126CS12",
"university":"rgtu"
}
]
Response data –
[
{
"id": 1,
"name": "Hiteshdo",
"rollNumber": "0126CS01",
"university": "rgtu"
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "Johnhjhjhjhj",
"rollNumber": "0126CS02",
"university": "rgtu"
},
{
"id": 3,
"name": "Mohankkkkkkkkkkkkkk",
"rollNumber": "0126CS03",
"university": "rgtu"
},
{
"id": 4,
"name": "Nagesh",
"rollNumber": "0126CS04",
"university": "rgtu"
},
{
"id": 5,
"name": "s",
"rollNumber": "0126CS05",
"university": "rgtu"
},
{
"id": 6,
"name": "Ranakum",
"rollNumber": "0126CS06",
"university": "rgtu"
},
{
"id": 7,
"name": "Roc",
"rollNumber": "0126CS07",
"university": "rgtu"
},
{
"id": 8,
"name": "Simpy",
"rollNumber": "0126CS08",
"university": "rgtu"
},
{
"id": 9,
"name": "Tiwari",
"rollNumber": "0126CS09",
"university": "rgtu"
},
{
"id": 10,
"name": "Appu",
"rollNumber": "0126CS10",
"university": "rgtu"
},
{
"id": 11,
"name": "Babloo",
"rollNumber": "0126CS11",
"university": "rgtu"
},
{
"id": 12,
"name": "Ga",
"rollNumber": "0126CS12",
"university": "rgtu"
}
]

Get operation. Let’s test we have records in DB or not.
API -http://localhost:9091/student/getall

Now delete a single record.

Delete all record which you are passing as request data.

Now we don’t have any record in database. Check DB and Again perform get operation. We should have empty array. We can show a message in a proper way using global error handler. See Example here.
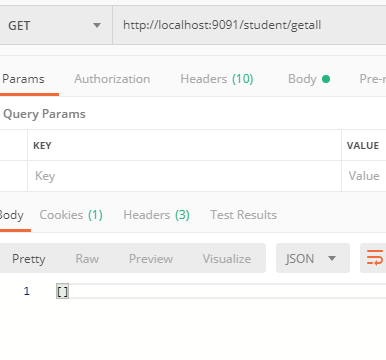
Still, we have one API to test.
First, call http://localhost:9091/student/saveall API then call http://localhost:9091/student/deleteall API. We should have below response and database shouldn’t contain any student records.

That’s all about Spring Data JPA CrudRepository delete() and deleteAll() Example.
You may like.
- Spring Data CrudRepository saveAll() and findAll().
- CrudRepository findAllById() Example Using Spring Boot.
- Spring Data CrudRepository existsById()
- Spring Data JPA CrudRepository findById()
- Spring Data CrudRepository save() Method.
- Sorting in Spring Data JPA using Spring Boot.
- Spring Data JPA example using spring boot.
- Spring Data JPA and its benefit.
Other Spring Data JPA and Hibernate tutorials.
- @Version Annotation Example In Hibernate.
- Hibernate Validator Constraints Example Using Spring Boot.
- @Temporal Annotation Example In Hibernate/Jpa Using Spring Boot.
- Hibernate Table Per Concrete Class Spring Boot.
- Hibernate Table Per Subclass Inheritance Spring Boot.
- Hibernate Single Table Inheritance using Spring Boot.
- One To One Mapping Annotation Example in Hibernate/JPA using Spring Boot and Oracle.
- One To One Bidirectional Mapping Example In Hibernate/JPA Using Spring Boot and Oracle.
- One To Many Mapping Annotation Example In Hibernate/JPA Using Spring Boot And Oracle.
- Many To One Unidirectional Mapping In Hibernate/JPA Annotation Example Using Spring Boot and Oracle.
- One To Many Bidirectional Mapping In Hibernate/JPA Annotation Example Using Spring Boot and Oracle.
- Many To Many Mapping Annotation Example In Hibernate/JPA Using Spring Boot And
Spring Data JPA CrudRepository() docs.



