In this post, we will see about Spring Data JPA @Modifying Annotation Example using Spring Boot and Oracle.
We will see how @Modifying annotation helps to execute DML (INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, etc) named parameter queries that we write using @Query annotations.
Introduction.
Generally, we use CrudRepository’s save() method to create or update an entity in Spring Data JPA. in this tutorial, we are going to see how to insert/update/get/delete records using @Query & @Modifying annotations.
Spring Data JPA provides @Modifying annotation, using this annotation we can write named parameters query using @Query annotation and we can insert, update, or delete an entity.
We will have four APIs to test our implementation as below. We will use postman for testing.
| Request Method | Rest APIs/End Points |
| POST | http://localhost:9091/student/insert |
| PUT | http://localhost:9091/student/update |
| GET | http://localhost:9091/student/{id} |
| DELETE | http://localhost:9091/student/delete |
Note – The method where we use @Modifying annotation, return type should be int or void. Otherwise, it will throw an exception(we will see later in detail). Insert, update, and delete an entity using Spring Data JPA @Modifying Annotation.
Consider we have an entity called Student.java.
package com.javatute.entity;
@Entity
public class Student {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private int id;
@Column(name = "student_name")
private String studentName;
@Column(name = "roll_number")
private String rollNumber;
@Column(name = "university")
String university;
}
Insert an entity using Spring Data JPA @Modifying annotation.
Repository code.
@Modifying
@Query(value = "insert into Student (id,student_name,roll_number, university) "
+ "VALUES(:id,:studentName,:rollNumber,:university)", nativeQuery = true)
public void insertStudentUsingQueryAnnotation(@Param("id") int id, @Param("studentName") String studentName,
@Param("rollNumber") String rollNumber, @Param("university") String university);Calling repository method.
@Override
@Transactional
public String insertStudent(Student student) {
int id = student.getId();
String studentName = student.getStudentName();
String rollNumber = student.getRollNumber();
String university = student.getUniversity();
studentRepository.insertStudentUsingQueryAnnotation(id, studentName, rollNumber, university);
return "Record inserted successfully using @Modifiying and @query Named Parameter";
}Update an entity using Spring Data JPA @Modifying annotation.
Repository code.
@Modifying
@Query("update Student s SET s.studentName = :studentName WHERE s.id = :id")
public void updateStudentUsingQueryAnnotation(@Param("studentName") String studentName, @Param("id") int id);Calling repository method to update entity using @Modifying.
@Transactional
public String updateStudent(Student student) {
studentRepository.updateStudentUsingQueryAnnotation(student.getStudentName(), student.getId());
return "Record updated successfully using @Modifiying and @query Named Parameter";
}Delete an entity using Spring Data JPA @Modifying annotation.
@Modifying
@Query("delete from Student s where s.id = :id")
public void deleteStudentUsingQueryAnnotation(@Param("id") int id);@Override
@Transactional
public String deleteStudent(Student student) {
studentRepository.deleteStudentUsingQueryAnnotation(student.getId());
return "Record deleted successfully using @Modifiying and @query Named Parameter";
}Retrieve an entity(No need to use @Modifying annotation).
@Query("select s from Student s where s.id = :id")
public Student findById(@Param("id") int id);@Transactional
public Student findById(int id) {
Student studentresponse = studentRepository.findById(id);
return studentresponse;
}Spring Data JPA @Modifying Annotation Example using Spring Boot and Oracle from scratch.
Open eclipse and create maven project, Don’t forget to check ‘Create a simple project (skip)’ click on next. Fill all details(GroupId – modifying, ArtifactId – modifying, and name – modifying) and click on finish. Keep packaging as the jar.
Modify pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>modifying</groupId> <artifactId>modifying</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>modifying</name> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.0.2.RELEASE</version> </parent> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.oracle</groupId> <artifactId>ojdbc6</artifactId> <version>11.2.0.3</version> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>
If you see any error for oracle dependency then follow these steps.
Directory structure.

Student.java
package com.javatute.entity;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
@Entity
public class Student {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private int id;
@Column(name = "student_name")
private String studentName;
@Column(name = "roll_number")
private String rollNumber;
@Column(name = "university")
String university;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getStudentName() {
return studentName;
}
public void setStudentName(String studentName) {
this.studentName = studentName;
}
public String getRollNumber() {
return rollNumber;
}
public void setRollNumber(String rollNumber) {
this.rollNumber = rollNumber;
}
public String getUniversity() {
return university;
}
public void setUniversity(String university) {
this.university = university;
}
}
StudentController.java
package com.javatute.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.javatute.entity.Student;
import com.javatute.service.StudentService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/student")
public class StudentController {
@Autowired
private StudentService studentService;
@RequestMapping(value = "/insert", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public String insertStudent(@RequestBody Student student) {
String response = studentService.insertStudent(student);
return response;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/update", method = RequestMethod.PUT)
@ResponseBody
public String updateStudent(@RequestBody Student student) {
String response = studentService.updateStudent(student);
return response;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public Student getStudent(@PathVariable int id) {
Student student = studentService.findById(id);
return student;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/delete", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@ResponseBody
public String deleteStudent(@RequestBody Student student) {
String response = studentService.deleteStudent(student);
return response;
}
}
StudentRepository.java – interface
package com.javatute.repository;
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.transaction.Transactional;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Modifying;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Query;
import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;
import org.springframework.data.repository.query.Param;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.javatute.entity.Student;
@Repository
public interface StudentRepository extends CrudRepository<Student, Serializable> {
@Modifying
@Transactional
@Query(value = "insert into Student (id,student_name,roll_number, university) "
+ "VALUES(:id,:studentName,:rollNumber,:university)", nativeQuery = true)
public void insertStudentUsingQueryAnnotation(@Param("id") int id, @Param("studentName") String studentName,
@Param("rollNumber") String rollNumber, @Param("university") String university);
@Modifying
@Transactional
@Query("update Student s SET s.studentName = :studentName WHERE s.id = :id")
public void updateStudentUsingQueryAnnotation(@Param("studentName") String studentName, @Param("id") int id);
@Modifying
@Transactional
@Query("delete from Student s where s.id = :id")
public void deleteStudentUsingQueryAnnotation(@Param("id") int id);
@Query("select s from Student s where s.id = :id")
public Student findById(@Param("id") int id);
}
StudentService.java – interface
package com.javatute.service;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import com.javatute.entity.Student;
@Component
public interface StudentService {
public String insertStudent(Student student);
public String updateStudent(Student student);
public String deleteStudent(Student student);
public Student findById(int id);
}
StudentServiceImpl.java
package com.javatute.impl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import com.javatute.entity.Student;
import com.javatute.repository.StudentRepository;
import com.javatute.service.StudentService;
@Service("studentServiceImpl")
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService {
@Autowired
private StudentRepository studentRepository;
@Override
@Transactional
public String insertStudent(Student student) {
int id = student.getId();
String studentName = student.getStudentName();
String rollNumber = student.getRollNumber();
String university = student.getUniversity();
studentRepository.insertStudentUsingQueryAnnotation(id, studentName, rollNumber, university);
return "Record inserted successfully using @Modifiying and @query Named Parameter";
}
@Transactional
public String updateStudent(Student student) {
studentRepository.updateStudentUsingQueryAnnotation(student.getStudentName(), student.getId());
return "Record updated successfully using @Modifiying and @query Named Parameter";
}
@Override
@Transactional
public String deleteStudent(Student student) {
studentRepository.deleteStudentUsingQueryAnnotation(student.getId());
return "Record deleted successfully using @Modifiying and @query Named Parameter";
}
@Transactional
public Student findById(int id) {
Student studentresponse = studentRepository.findById(id);
return studentresponse;
}
}
SpringMain.java
package com.javatute.main;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.domain.EntityScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
@SpringBootApplication
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.javatute.*")
@EntityScan("com.javatute.*")
public class SpringMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringMain.class, args);
}
}
JpaConfig.java
package com.javatute.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.config.EnableJpaRepositories;
@Configuration
@EnableJpaRepositories(basePackages = "com.javatute.repository")
public class JpaConfig {
}
application.properties
# Connection url for the database spring.datasource.url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:XE spring.datasource.username=SYSTEM spring.datasource.password=oracle spring.datasource.driver-class-name=oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver # Show or not log for each sql query spring.jpa.show-sql = true spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.format_sql=true spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto =create spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.Oracle10gDialect server.port = 9091 #show sql values #logging.level.org.hibernate.type.descriptor.sql=trace hibernate.show_sql = true #spring.jpa.hibernate.logging.level.sql =FINE #show sql statement #logging.level.org.hibernate.SQL=debug
Let’s run the SpringMain class(run as java application).
Testing of example using Postman.
Perform insert operation first using below REST API.
POST http://localhost:9091/student/insert
Request Data –
{
"id": 1,
"studentName": "john",
"rollNumber": "0126CS01",
"university": "rgtu"
}
Response data.

Perform update operation using below REST API.
PUT – http://localhost:9091/student/update
Request Data –
{
"id": 1,
"studentName": "john_updated_name",
"rollNumber": "0126CS01",
"university": "rgtu"
}
Response Data.

Perform Get operation using below REST API.
GET – http://localhost:9091/student/{id}
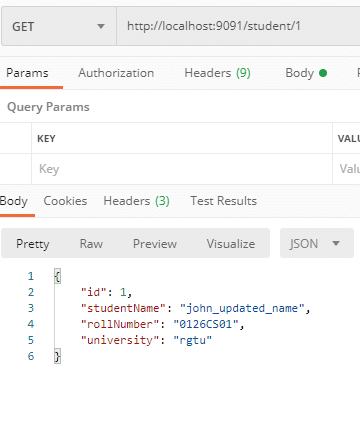
Perform Delete operation using below REST API.
DELETE- http://localhost:9091/student/delete
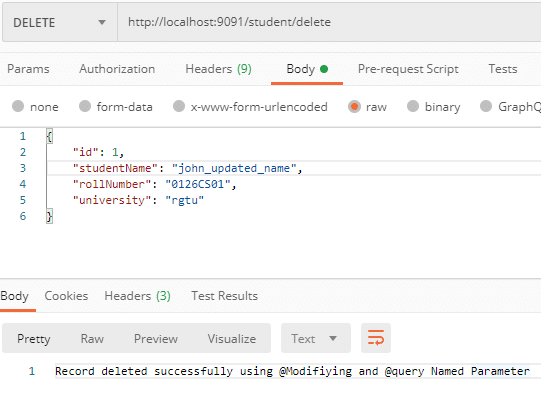
Generated query.
Hibernate:
insert
into
Student
(id,student_name,roll_number, university)
VALUES
(?,?,?,?)
Hibernate:
update
student
set
student_name=?
where
id=?
Hibernate:
select
student0_.id as id1_0_,
student0_.roll_number as roll_number2_0_,
student0_.student_name as student_name3_0_,
student0_.university as university4_0_
from
student student0_
where
student0_.id=?
Hibernate:
delete
from
student
where
id=?
Understanding difference while updating an entity using CrudRepository’s save() method and @Modifying annotation.
we are going to update the name field of the Student entity using save() method and @Modifying annotation. We will see what is the difference in both cases.
In StudentServiceImpl.java
@Transactional
public String updateStudent(Student student) {
//studentRepository.updateStudentUsingQueryAnnotation(student.getStudentName(), student.getId());
studentRepository.save(student);
return "Record updated successfully using save() method";
}
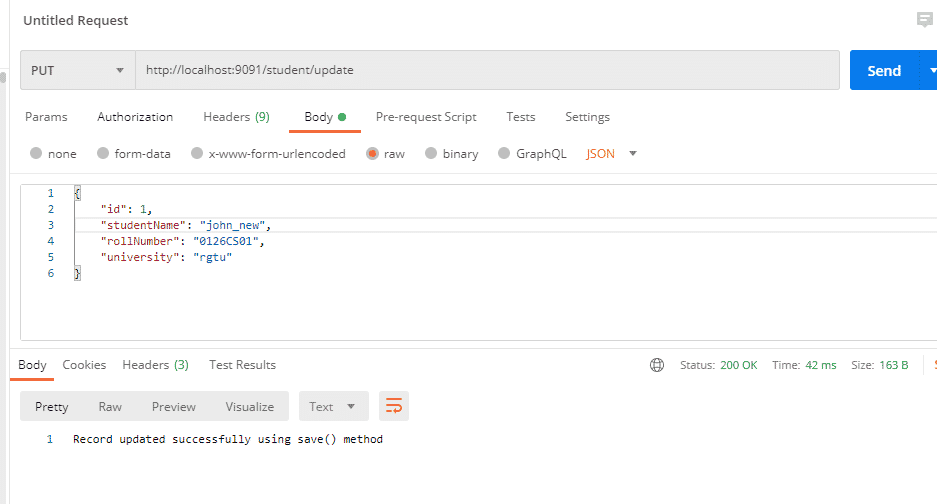
The query generated while updating the student using the save() method.
Hibernate:
select
student0_.id as id1_0_0_,
student0_.roll_number as roll_number2_0_0_,
student0_.student_name as student_name3_0_0_,
student0_.university as university4_0_0_
from
student student0_
where
student0_.id=?
Hibernate:
update
student
set
roll_number=?,
student_name=?,
university=?
where
id=?
Now we will update the student name using @Modifying annotation.

The query generated while updating the student using the @Modifying annotation.
Hibernate:
update
student
set
student_name=?
where
id=?
In the case of save() method, first it will retrieve the entity then the update statement will execute. In the case of @Modifying annotation, it will only execute an update statement.
Note – The same thing applies to delete operation. If we delete an entity using Repository delete() method first select statement will get executed then the delete statement will get executed. But if we try to delete @Modifying then only delete statement.
Overriding @Transactional(readOnly = true) behavior using @Modifying Annotation.
When we use @Transactional (readOnly = true) then we will not able to perform update or delete operation. But we can override readOnly behavior using @Modifying annotation. For example, suppose @Transactional annotation has been used with class level or interface level as below and we want to override readOnly behavior for one method(we don’t want to apply readOnly true for updateStudentUsingQueryAnnotation() method).
@Repository
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public interface StudentRepository extends CrudRepository<Student,Serializable> {
List<Book> findByBookName(String bookName);
@Modifying
@Query("update Student s SET s.studentName = :studentName WHERE s.id = :id")
public void updateStudentUsingQueryAnnotation(@Param("studentName") String studentName, @Param("id") int id);
}
Some Basic Points about @Modifying Annotation.
The @Modifying annotation is available in org.springframework.data.jpa.repository and can be used with class and method.
The @Modifying annotation contains two elements flushAutomatically and clearAutomatically. Both have default values as false.
Using flushAutomatically and clearAutomatically with @Modifying annotation example.
@Modifying(flushAutomatically = true, clearAutomatically = true)@Query("update Student s SET s.studentName = :studentName WHERE s.id = :id")public void updateStudentUsingQueryAnnotation(@Param("studentName") String studentName, @Param("id") int id);
If we define flushAutomatically = true that means, the underlying persistence context should flush before executing the modifying query.
When we define clearAutomatically = true that means, clear the underlying persistence context after executing the modifying query.
Note – Here modifying query means @Query("update Student s SET s.studentName = :studentName WHERE s.id = :id").
If we define some different return types than void or int or Integer with the method which is annotated with @Modifying then it will throw java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Modifying queries can only use void or int/Integer as return type exception. For example, the below code snippet will throw an exception.
@Modifying@Query("UPDATE Student s SET s.studentName = :studentName WHERE s.id = :id")public Student updateStudentUsingQueryAnnotation(@Param("studentName") String studentName, @Param("id") int id);
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Modifying queries can only use void or int/Integer as return type!
at org.springframework.util.Assert.isTrue(Assert.java:116) ~[spring-core-5.0.6.RELEASE.jar:5.0.6.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.query.JpaQueryExecution$ModifyingExecution.<init>(JpaQueryExecution.java:242) ~[spring-data-jpa-2.0.7.RELEASE.jar:2.0.7.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.query.AbstractJpaQuery.getExecution(AbstractJpaQuery.java:157) ~[spring-data-jpa-2.0.7.RELEASE.jar:2.0.7.RELEASE]
at org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.query.AbstractJpaQuery.execute(AbstractJpaQuery.java:125) ~[spring-data-jpa-2.0.7.RELEASE.jar:2.0.7.RELEASE]
That’s all about Spring Data JPA @Modifying Annotation Example Using Spring Boot and Oracle. In case of any doubt or query please leave a comment.
Download the source code from github.
You may like.
- Spring Data JPA greater than Example
- Spring Data JPA less than Example
- Spring Data JPA IsNull Example Using Spring Boot
- Spring Data findById() Vs getOne()
- Spring Data JPA CrudRepository findById()
- Spring Data JPA JpaRepository getOne()
- Spring Data CrudRepository saveAll() and findAll().
- Spring Data CrudRepository existsById()
- Spring Data JPA delete() vs deleteInBatch()
- Spring Data JPA deleteAll() Vs deleteAllInBatch()
- Spring Data JPA JpaRepository deleteAllInBatch()
- Spring Data JPA deleteInBatch() Example
- Spring Data JPA JpaRepository saveAndFlush() Example
Hibernate/JPA association mapping example using Spring Boot.
- One To One Mapping Annotation Example in Hibernate/JPA using Spring Boot and Oracle.
- One To One Bidirectional Mapping Example In Hibernate/JPA Using Spring Boot and Oracle.
- One To Many Mapping Annotation Example In Hibernate/JPA Using Spring Boot And Oracle.
- Many To One Unidirectional Mapping In Hibernate/JPA Annotation Example Using Spring Boot and Oracle.
- One To Many Bidirectional Mapping In Hibernate/JPA Annotation Example Using Spring Boot and Oracle.
- Many To Many Mapping Annotation Example In Hibernate/JPA Using Spring Boot And Oracle.
Spring Data JPA @Modifying docs.



