In this tutorial, we will see @OneToMany orphanRemoval true example in Hibernate/JPA using Spring Boot and Oracle.
Basic points about orphanRemoval true.
- The orphanRemoval true is an optional element which has been defined in @OneToMany annotation. it has been introduced in JPA 2.0.
- The default value of orphanRemoval is false.
public @interface OneToMany { boolean orphanRemoval() default false;}
- Example to use
orphanRemoval = true.
@OneToMany(cascade = CascadeType.ALL, fetch = FetchType.LAZY, orphanRemoval = true)@JoinColumn(name = "book_id", referencedColumnName = "bookId")private List<Story> storyList = new ArrayList<>();
- Consider two entities (Book/Parent and Story/Child) are in OneToMany mapping and we are using orphanRemoval = true. If we remove Story entities(child entities) from Book entity the story/child record will be deleted automatically from the database. In case if we don’t use orphanRemoval = true the child entities will not get deleted from the database only foreign key will updated to null(we will see later in details).
Understanding Hibernate/JPA @OneToMany orphanRemoval = true.
In this section, we will see what exactly orphanRemoval = true does if we use with @OneToMany annotation. Suppose we have two entities called Book.java and Story.java. Both are in OneToMany relationship(One book can have multiple stories).
Book.java
@Entity
public class Book {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private int bookId;
@Column(name = "book_name")
private String bookName;
@OneToMany(cascade = CascadeType.ALL, fetch = FetchType.LAZY, orphanRemoval = true)
@JoinColumn(name = "book_id", referencedColumnName = "bookId")
private List<Story> storyList = new ArrayList<>();
}
Story.java
@Entity
public class Story {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private int storyId;
@Column(name = "story_name")
private String storyName;
}
Also, we have BookServiceImpl.java class which contains logic to save and delete.
package com.hibernatejpa.impl;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import com.hibernatejpa.entity.Book;
import com.hibernatejpa.repository.BookRepository;
import com.hibernatejpa.service.BookService;
@Service("bookServiceImpl")
public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService {
@Autowired
private BookRepository bookRepository;
@Transactional
public Book saveBook(Book book) {
book = bookRepository.save(book);
return book;
}
public String removeStoriesFromBook(int bookId) {
Optional<Book> bookResponse = bookRepository.findById(bookId);
Book book = bookResponse.get();
book.getStoryList().removeAll(book.getStoryList());
bookRepository.save(book);
return "Record deleted successfully";
}
}
Now we are using orphanRemoval = true in Book.java with storyList field. If we try to remove story entities(child entities) from Book entity(Parent entity)(line number 30), the story/child record will be deleted automatically from the database.
If we don’t use orphanRemoval = true and will perform the same operation it will not delete story/child record from the database.
We will see the complete example from scratch later. For now, just see what will happen if we perform save operation and try to remove Stories from Book in both cases.
With orphanRemoval = true
http://localhost:9091/book/savebook

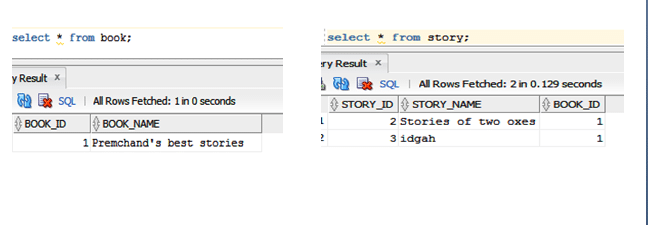
We should have some record in the database.
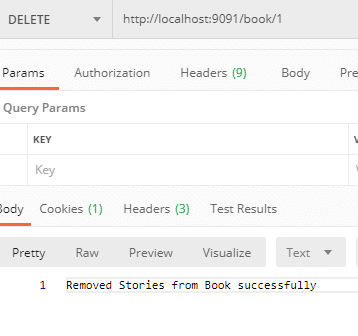
Removing Stories from Book using below API.
Let’s check the database.

Generated Query with orphanRemoval = true.
Hibernate: select book0_.book_id as book_id1_0_0_, book0_.book_name as book_name2_0_0_ from book book0_ where book0_.book_id=?
Hibernate: select storylist0_.book_id as book_id3_1_0_, storylist0_.story_id as story_id1_1_0_, storylist0_.story_id as story_id1_1_1_, storylist0_.story_name as story_name2_1_1_ from story storylist0_ where storylist0_.book_id=?
Hibernate: update story set book_id=null where book_id=?
Hibernate: delete from story where story_id=?
Hibernate: delete from story where story_id=?
Without orphanRemoval = true
Let’s do the same steps except don’t use orphanRemoval = true.
http://localhost:9091/book/savebook

We should have some record in the database.

Removing Stories from Book using below API.


Generated query without orphanRemoval = true.
Hibernate: select book0_.book_id as book_id1_0_0_, book0_.book_name as book_name2_0_0_ from book book0_ where book0_.book_id=?
Hibernate: select storylist0_.book_id as book_id3_1_0_, storylist0_.story_id as story_id1_1_0_, storylist0_.story_id as story_id1_1_1_, storylist0_.story_name as story_name2_1_1_ from story storylist0_ where storylist0_.book_id=?
Hibernate: update story set book_id=null where book_id=?
Different between cascade = CascadeType.REMOVE and orphanRemoval = true.
For beginners, it might little be confusing what is the difference between cascade = CascadeType.REMOVE and orphanRemoval = true.
If we don’t use CascadeType.REMOVE then we will not able to delete child entity along with the parent. We have a separate detailed post here.
@OneToMany orphanRemoval true example in Hibernate/JPA Using Sping Boot and Oracle.
Create maven project, Don’t forget to check ‘Create a simple project (skip)’click on next. Fill all details(GroupId – orphanremoval, ArtifactId – orphanremoval and name – orphanremoval) and click on finish. Keep packaging as the jar.
Modify the pom.xml with the below code.
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>orphanremoval</groupId>
<artifactId>orphanremoval</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>orphanremoval</name>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.2.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.oracle</groupId>
<artifactId>ojdbc6</artifactId>
<version>11.2.0.3</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>${project.artifactId}</finalName>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.1</version>
<configuration>
<fork>true</fork>
<executable>C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_131\bin\javac.exe</executable>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Note – In pom.xml we have defined javac.exe path in configuration tag. You need to change accordingly i.e where you have installed JDK.
If you see any error for oracle dependency then follow these steps.
Define entity class i.e Book.java and Story.java.
Book.java
package com.hibernatejpa.entity;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.FetchType;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.ManyToMany;
import javax.persistence.OneToMany;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnoreProperties;
@Entity
public class Book {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private int bookId;
@Column(name = "book_name")
private String bookName;
@OneToMany(cascade = CascadeType.ALL, fetch = FetchType.LAZY, orphanRemoval = true)
@JoinColumn(name = "book_id", referencedColumnName = "bookId")
private List<Story> storyList = new ArrayList<>();
public int getBookId() {
return bookId;
}
public void setBookId(int bookId) {
this.bookId = bookId;
}
public String getBookName() {
return bookName;
}
public void setBookName(String bookName) {
this.bookName = bookName;
}
public List<Story> getStoryList() {
return storyList;
}
public void setStoryList(List<Story> storyList) {
this.storyList = storyList;
}
}
Story.java
package com.hibernatejpa.entity;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
@Entity
public class Story {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private int storyId;
@Column(name = "story_name")
private String storyName;
public int getStoryId() {
return storyId;
}
public void setStoryId(int storyId) {
this.storyId = storyId;
}
public String getStoryName() {
return storyName;
}
public void setStoryName(String storyName) {
this.storyName = storyName;
}
}
Define the repository interface extending CrudRepository.
BookRepository.java
package com.hibernatejpa.repository;
import java.io.Serializable;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.hibernatejpa.entity.Book;
@Repository
public interface BookRepository extends JpaRepository<Book,Serializable> {
public Book findByBookId(int bookId);
}
Define service interface i.e BookService.java
package com.hibernatejpa.service;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import com.hibernatejpa.entity.Book;
@Component
public interface BookService {
public Book saveBook(Book book);
public String removeStoryFromBook(int id);
}
Define service implementation class.
BookServiceImpl.java
package com.hibernatejpa.impl;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import com.hibernatejpa.entity.Book;
import com.hibernatejpa.repository.BookRepository;
import com.hibernatejpa.service.BookService;
@Service("bookServiceImpl")
public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService {
@Autowired
private BookRepository bookRepository;
@Transactional
public Book saveBook(Book book) {
book = bookRepository.save(book);
return book;
}
public String removeStoryFromBook(int bookId) {
Optional<Book> bookResponse = bookRepository.findById(bookId);
Book book = bookResponse.get();
book.getStoryList().removeAll(book.getStoryList());
bookRepository.save(book);
return "Removed Stories from Book successfully";
}
}
Note – See here more about @Component, @Controller, @Service and @Repository annotations here.
Define the controller class or endpoint.
BookController.java
package com.hibernatejpa.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.hibernatejpa.entity.Book;
import com.hibernatejpa.service.BookService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/book")
public class BookController {
@Autowired
private BookService bookService;
@RequestMapping(value = "/savebook", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public Book saveBook(@RequestBody Book book) {
Book bookResponse = bookService.saveBook(book);
return bookResponse;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/{bookId}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@ResponseBody
public String deleteBook(@PathVariable int bookId) {
String bookResponse = bookService.removeStoryFromBook(bookId);
return bookResponse;
}
}
Note – See more details about @Controller and RestController here.
Define the JpaConfig.java
package com.hibernatejpa.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.config.EnableJpaRepositories;
@Configuration
@EnableJpaRepositories(basePackages = "com.hibernatejpa.repository")
public class JpaConfig {
}
Define the SpringMain.java
package com.hibernatejpa.main;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.domain.EntityScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
@SpringBootApplication
@ComponentScan(basePackages="com.hibernatejpa.*")
@EntityScan("com.hibernatejpa.*")
public class SpringMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringMain.class, args);
}
}
And finally, we have an application.properties file where we have database details.
application.properties
# Connection url for the database spring.datasource.url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:XE spring.datasource.username=SYSTEM spring.datasource.password=oracle3 spring.datasource.driver-class-name=oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver # Show or not log for each sql query spring.jpa.show-sql = true spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto =create spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.Oracle10gDialect server.port = 9091
We are almost done. Just build the project once running the main method. Open git bash or cmd and Run mvn clean install.
Let’s deploy the application running SpringMain class as a java application.
Sample request JSON data to test the end point.
{
"bookName": "Premchand's best stories",
"storyList": [{
"storyName": "Stories of two oxes"
},
{
"storyName": "idgah"
}
]
}
POST – http://localhost:9091/book/savebook
DELETE – http://localhost:9091/book/1
That’s all about @OneToMany orphanRemoval true example in Hibernate/JPA Using Spring Boot and Oracle.
You may like.
- JPA Cascade Types example using Spring Boot.
- JPA EntityManager persist() and merge() method.
- @ElementCollection Example in Hibernate/JPA Using Spring Boot.
- Hibernate First Level Cache example using Spring Boot.
Other Tutorial.
- Hibernate Table Per Concrete Class Spring Boot.
- Hibernate Table Per Subclass Inheritance Spring Boot.
- Hibernate Single Table Inheritance using Spring Boot.
- One To One Mapping Annotation Example in Hibernate/JPA using Spring Boot and Oracle.
- One To One Bidirectional Mapping Example In Hibernate/JPA Using Spring Boot and Oracle.
- One To Many Mapping Annotation Example In Hibernate/JPA Using Spring Boot And Oracle.
- Many To One Unidirectional Mapping In Hibernate/JPA Annotation Example Using Spring Boot and Oracle.
- One To Many Bidirectional Mapping In Hibernate/JPA Annotation Example Using Spring Boot and Oracle.
- Many To Many Mapping Annotation Example In Hibernate/JPA Using Spring Boot And
OneToMany orphanRemoval true docs.



