Here we will see @RestController and @Controller annotation example in Spring Boot.
Basic points about @RestController and @Controller annotation.
@RestController annotation.
- This annotation introduced in Spring 4.0, available in org.springframework.web.bind.annotation package.
- It has one optional element i.e value.
- We use this annotation with the class.
- This annotation is a combined form of @Controller and @ResponseBody
- Internal implementation –
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Controller
@ResponseBody
public @interface RestController {
}
@Controller annotation.
- This annotation introduced in Spring 2.5, available in org.springframework.stereotype package.
- It has one optional element i.e value.
- We use this annotation with the class, in case of this annotation we need to use @ResponseBody explicitly.
- Internal implementation –
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface Controller {
}
Note – What will happen if we use @RestController with the method or interface? With the method, it will give compilation error but if we use this annotation with an interface no compilation error. If we use @RestController with the interface then we need to provide corresponding implementation classes.
@RestController annotation example.
prerequisites –
- JDK 1.8
- Eclipse
- maven
- postman
Create maven project, Don’t forget to check ‘Create a simple project (skip)’click on next. Fill all details(GroupId – restcontrollerexample, ArtifactId – restcontrollerexample and name – restcontrollerexample) and click on finish. Keep packaging as the jar.
Make sure we have a correct pom.xml.
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>restcontrollerexample</groupId>
<artifactId>restcontrollerexample</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>restcontrollerexample</name>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.2.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
Define Contoller(RestControllerExampleEndPoint.java), SpringBootMain(SpringRestControllerExample.java), and Entity class(Book.java).
RestControllerExampleEndPoint.java
package com.restcontroller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.entity.Book;
@RestController
public class RestControllerExampleEndPoint {
@RequestMapping(value = "/simpleuri",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public Book getBook() {
Book book = new Book();
book.setBookId(109);
book.setBookName("book1");
book.setBookPrice("100");
return book;
}
}
SpringRestControllerExample.java
package com.restcontroller;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.domain.EntityScan;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringRestControllerExample {
public static void main(final String[] args) {
final ConfigurableApplicationContext configurableApplicationContext = SpringApplication
.run(SpringRestControllerExample.class, args);
}
}
Book.java
package com.entity;
public class Book {
int bookId;
String bookName;
String bookPrice;
public int getBookId() {
return bookId;
}
public void setBookId(int bookId) {
this.bookId = bookId;
}
public String getBookName() {
return bookName;
}
public void setBookName(String bookName) {
this.bookName = bookName;
}
public String getBookPrice() {
return bookPrice;
}
public void setBookPrice(String bookPrice) {
this.bookPrice = bookPrice;
}
}
If you encounter any port related issue, define application.properties and change the port.
application.properties
server.port = 9093
Run the main class(SpringRestControllerExample.java).
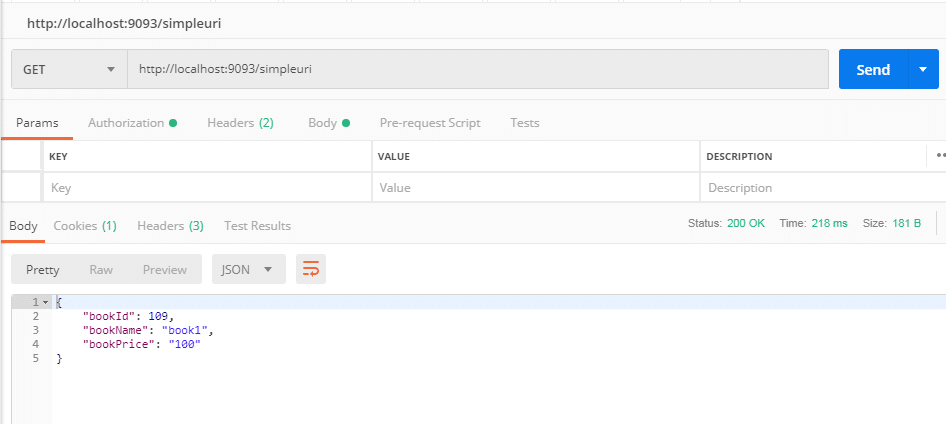
Call rest URI(http://localhost:9093/simpleuri) from postman
@Controller annotation example.
Let’s modify the controller class, we will not use @Responsebody annotation and see what happens.
package com.restcontroller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.entity.Book;
@Controller
public class RestControllerExampleEndPoint {
@RequestMapping(value = "/simpleuri",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public Book getBook() {
Book book = new Book();
book.setBookId(109);
book.setBookName("book1");
book.setBookPrice("100");
return book;
}
}
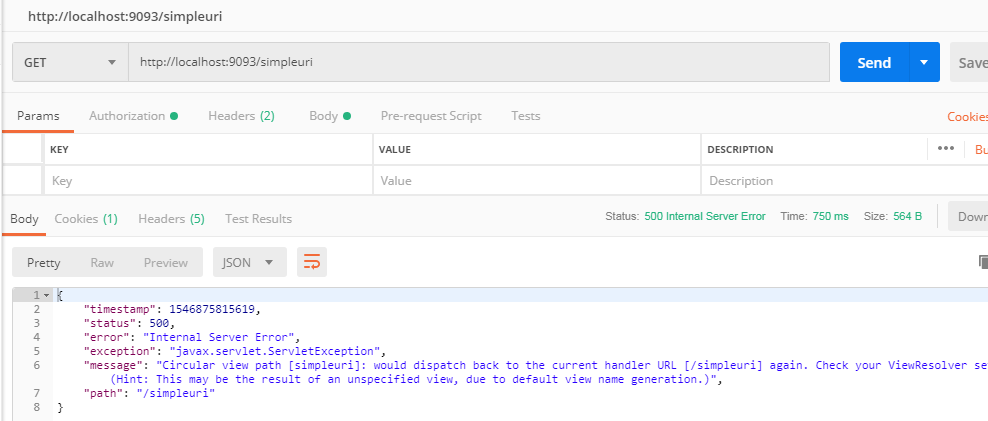
Run the main class and hit the rest URI from the postman.
Let’s use @ResponseBody with method or class.
package com.restcontroller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.entity.Book;
@Controller
@ResponseBody
public class RestControllerExampleEndPoint {
@RequestMapping(value = "/simpleuri",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public Book getBook() {
Book book = new Book();
book.setBookId(109);
book.setBookName("book1");
book.setBookPrice("100");
return book;
}
}
Again run the main class.
Yes, we have a response now.
That’s all about @RestController and @Controller annotation example in Spring Boot.
You may like.
- @RequestMapping annotation example In Spring Boot.
- @RequestBody and @ResponseBody annotation example in Spring Boot.
- @PathVariable and @RequestParam annotations in Spring Boot.
- @RequestHeader annotation example by using Spring Boot.
- @SpringBootApplication annotation example in Spring Boot.
- @Component, @Controller, @Service and @Repository annotations example using Spring Boot.
- @Configuration annotation example using spring boot.
- @ComponentScan example in spring boot.